Init
This commit is contained in:
BIN
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/水下逻辑判断.jpg
Normal file
BIN
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/水下逻辑判断.jpg
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 56 KiB |
BIN
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/水下逻辑判断2.jpg
Normal file
BIN
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/水下逻辑判断2.jpg
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.6 KiB |
76
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/海洋SSS效果论文笔记.md
Normal file
76
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/海洋SSS效果论文笔记.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
## 论文与相关资料
|
||||
### 寒霜的快速SSS
|
||||
在GDCVault中搜索对应的演讲,之后就可以下载了。一些PPT比较大,可以直接去控件里找下载地址。
|
||||
|
||||
https://www.slideshare.net/colinbb/colin-barrebrisebois-gdc-2011-approximating-translucency-for-a-fast-cheap-and-convincing-subsurfacescattering-look-7170855
|
||||
|
||||
#### 视频
|
||||
https://www.gdcvault.com/play/1014536/Approximating-Translucency-for-a-Fast
|
||||
|
||||
因为视频是blob模式的,所以可以去下面的网站下载:
|
||||
http://downloadblob.com/
|
||||
|
||||
#### ppt
|
||||
https://twvideo01.ubm-us.net/o1/vault/gdc2011/slides/Colin_BarreBrisebois_Programming_ApproximatingTranslucency.pptx
|
||||
|
||||
### SIGGRAPH2019ppt
|
||||
http://advances.realtimerendering.com/s2019/index.htm
|
||||
|
||||
## Approximating Translucency for a Fast, Cheap and Convincing Subsurface Scattering Look
|
||||
### 数据管理
|
||||
数据可以分成材质相关与灯光类型相关。在寒霜中材质相关会使用GBuffer传递(UE4可以使用CustomData吧),光类型相关会在LightPass中传递。
|
||||
|
||||
### 计算厚度值
|
||||
通过AO的方式来计算厚度:
|
||||
- 反转表面法线
|
||||
- 渲染AO
|
||||
- 反转颜色最后渲染到贴图中
|
||||
|
||||
### 技术细节
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
LT应该是Light Translucency的意思。v代表Vector,f代表float,i代表int。
|
||||
```
|
||||
half3 vLTLight = vLight + vNormal * fLTDistortion;
|
||||
half fLTDot = pow(saturate(dot(vEye, -vLTLight)), iLTPower) * fLTScale;
|
||||
half3 fLT = fLightAttenuation * (fLTDot + fLTAmbient) * fLTThickness;
|
||||
outColor.rgb += cDiffuseAlbedo * cLightDiffuse * fLT;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### fLTAmbient
|
||||
Ambient项,代表了始终存的各个方向的透射值。材质相关变量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### iLTPower
|
||||
强度衰减项,直接透射强度。与视口相关。可以通过预计算进行优化。材质相关变量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### fLTDistortion
|
||||
透射方向形变项,用于模拟光线传输的不规则的效果,类似于毛玻璃的效果。主要的功能是控制法线对于透射光方向的影响。与视口相关。材质相关变量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### fLTThickness
|
||||
厚底项,预计算的Local坐标的表面厚度值。材质相关变量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### fLTScale
|
||||
缩放项,用于缩放直接透射效果。视口相关。灯光相关变量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 最终效果
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### GBuffer设计
|
||||
最低的要求是GBufer中使用8位位宽灰度贴图的方式来存储translucency。使用24位位宽以颜色贴图的方式,可以实现材质对于不同光谱的光线不同的散射效果。
|
||||
|
||||
### 技术缺点
|
||||
因为是一种近似技术,所以只适合在凸物体上演示。这种技术对变形物体不起作用,因为需要烘焙厚度贴图。此外,我们可以使用实时AO算法配合倒置法线来计算厚度。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
PS.该技术的详细描述可以在《GPU PRO2》中找到。
|
||||
202
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/海洋论文笔记.md
Normal file
202
03-UnrealEngine/Rendering/Shader/Effect/Ocean/海洋论文笔记.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
|
||||
## UE4 渲染功能探究
|
||||
New: Planar Reflections
|
||||
New: High Quality Reflections
|
||||
|
||||
## UE4.26 SingleLayerWater笔记
|
||||
官方论坛讨论
|
||||
|
||||
https://forums.unrealengine.com/development-discussion/rendering/1746626-actually-realistic-water-shader#post1789028
|
||||
### SingleLayerCommon.ush
|
||||
计算光照强度、透明度。
|
||||
struct WaterVolumeLightingOutput
|
||||
{
|
||||
float3 Luminance;
|
||||
float3 WaterToSceneTransmittance;
|
||||
float3 WaterToSceneToLightTransmittance;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Output.Luminance = WaterVisibility * (ScatteredLuminance + Transmittance * BehindWaterSceneLuminance);
|
||||
Output.WaterToSceneTransmittance = Transmittance;
|
||||
Output.WaterToSceneToLightTransmittance;
|
||||
|
||||
目前没有开启RayMarching,所以核心代码为:
|
||||
```
|
||||
const float3 OpticalDepth = ExtinctionCoeff * BehindWaterDeltaDepth;
|
||||
float3 Transmittance = exp(-OpticalDepth);
|
||||
float3 ScatteredLuminance = ScatteringCoeff * (AmbScattLuminance + SunScattLuminance * DirectionalLightShadow);
|
||||
ScatteredLuminance = (ScatteredLuminance - ScatteredLuminance * Transmittance) / ExtinctionCoeffSafe;
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply Fresnel effect to out-scattering towards the view
|
||||
ScatteredLuminance *= CameraIsUnderWater ? 1.0 : (1.0 - EnvBrdf); // Under water is less visible due to Fresnel effect
|
||||
Transmittance *= CameraIsUnderWater ? (1.0 - EnvBrdf) : 1.0; // Above " " " " "
|
||||
|
||||
// Add single in-scattering apply colored transmittance to scene color
|
||||
Output.Luminance = WaterVisibility * (ScatteredLuminance + Transmittance * (BehindWaterSceneLuminance* ColorScaleBehindWater));
|
||||
Output.WaterToSceneTransmittance = Transmittance;
|
||||
Output.WaterToSceneToLightTransmittance = Transmittance * MeanTransmittanceToLightSources;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
const float BehindWaterDeltaDepth = CameraIsUnderWater ? WaterDepth : max(0.0f, SceneDepth - WaterDepth);
|
||||
|
||||
const float3 ScatteringCoeff = max(0.0f, GetSingleLayerWaterMaterialOutput0(MaterialParameters));
|
||||
const float3 AbsorptionCoeff = max(0.0f, GetSingleLayerWaterMaterialOutput1(MaterialParameters));
|
||||
const float PhaseG = clamp(GetSingleLayerWaterMaterialOutput2(MaterialParameters), -1.0f, 1.0f);
|
||||
//Sample the optional Material Input ColorScaleBehindWater and fade it out at shorelines to avoid hard edge intersections
|
||||
float3 ColorScaleBehindWater = lerp(1.0f, max(0.0f, GetSingleLayerWaterMaterialOutput3(MaterialParameters)), saturate(BehindWaterDeltaDepth * 0.02f));
|
||||
|
||||
const float3 ExtinctionCoeff = ScatteringCoeff + AbsorptionCoeff;
|
||||
// Max to avoid division by 0 with the analytical integral below.
|
||||
// 1e-5 is high enough to avoid denorms on mobile
|
||||
const float3 ExtinctionCoeffSafe = max(ScatteringCoeff + AbsorptionCoeff, 1e-5);
|
||||
|
||||
float DirLightPhaseValue = 0.0f; // Default when Total Internal Reflection happens.
|
||||
{
|
||||
#if SIMPLE_SINGLE_LAYER_WATER
|
||||
DirLightPhaseValue = IsotropicPhase();
|
||||
#else
|
||||
float IorFrom = 1.0f; // assumes we come from air
|
||||
float IorTo = DielectricF0ToIor(DielectricSpecularToF0(Specular)); // Wrong if metal is set to >1. But we still keep refraction on the water surface nonetheless.
|
||||
const float relativeIOR = IorFrom / IorTo;
|
||||
float3 UnderWaterRayDir = 0.0f;
|
||||
if (WaterRefract(MaterialParameters.CameraVector, MaterialParameters.WorldNormal, relativeIOR, UnderWaterRayDir))
|
||||
{
|
||||
DirLightPhaseValue = SchlickPhase(PhaseG, dot(-ResolvedView.DirectionalLightDirection.xyz, UnderWaterRayDir));
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We also apply transmittance from light to under water surface. However, the scene has been lit by many sources already.
|
||||
// So the transmittance toabove surface is simply approximated using the travel distance from the scene pixel to the water top, assuming a flat water surface.
|
||||
// We cannot combine this transmittance with the transmittance from view because this would change the behavior of the analytical integration of light scattering integration.
|
||||
const float3 BehindWaterSceneWorldPos = SvPositionToWorld(float4(MaterialParameters.SvPosition.xy, SceneDeviceZ, 1.0));
|
||||
const float DistanceFromScenePixelToWaterTop = max(0.0, MaterialParameters.AbsoluteWorldPosition.z - BehindWaterSceneWorldPos.z);
|
||||
const float3 MeanTransmittanceToLightSources = exp(-DistanceFromScenePixelToWaterTop * ExtinctionCoeff);
|
||||
|
||||
#if SIMPLE_SINGLE_LAYER_WATER
|
||||
const float3 BehindWaterSceneLuminance = 0.0f; // Cannot read back the scene color in this case
|
||||
#else
|
||||
// We use the pixel SvPosition instead of the scene one pre refraction/distortion to avoid those extra ALUs.
|
||||
float3 BehindWaterSceneLuminance = SceneColorWithoutSingleLayerWaterTexture.SampleLevel(SceneColorWithoutSingleLayerWaterSampler, ViewportUV, 0).rgb;
|
||||
BehindWaterSceneLuminance = MeanTransmittanceToLightSources * (USE_PREEXPOSURE ? ResolvedView.OneOverPreExposure : 1.0f) * BehindWaterSceneLuminance;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
float3 SunScattLuminance = DirLightPhaseValue * SunIlluminance;
|
||||
float3 AmbScattLuminance = IsotropicPhase() * AmbiantIlluminance;
|
||||
|
||||
#define VOLUMETRICSHADOW 0
|
||||
#if !VOLUMETRICSHADOW || SIMPLE_SINGLE_LAYER_WATER
|
||||
|
||||
const float3 OpticalDepth = ExtinctionCoeff * BehindWaterDeltaDepth;
|
||||
float3 Transmittance = exp(-OpticalDepth);
|
||||
float3 ScatteredLuminance = ScatteringCoeff * (AmbScattLuminance + SunScattLuminance * DirectionalLightShadow);
|
||||
ScatteredLuminance = (ScatteredLuminance - ScatteredLuminance * Transmittance) / ExtinctionCoeffSafe;
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
// TODO Make the volumetric shadow part work again
|
||||
float3 Transmittance = 1.0f;
|
||||
float3 ScatteredLuminance = 0.0f;
|
||||
const float RayMarchMaxDistance = min(BehindWaterDeltaDepth, 200.0f); // 20 meters
|
||||
const float RayMarchStepSize = RayMarchMaxDistance / 10.0f; // Less samples wil lresult in a bit brighter look due to TransmittanceToLightThroughWater being 1 on a longer first sample. Would need it part of analiytical integration
|
||||
const float ShadowDither = RayMarchStepSize * GBufferDither;
|
||||
for (float s = 0.0f; s < RayMarchMaxDistance; s += RayMarchStepSize)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Only jitter shadow map sampling to not lose energy on first sample
|
||||
float Shadow = ComputeDirectionalLightDynamicShadowing(MaterialParameters.AbsoluteWorldPosition - (s + ShadowDither)*MaterialParameters.CameraVector, GBuffer.Depth);
|
||||
|
||||
float3 WP = MaterialParameters.AbsoluteWorldPosition - s * MaterialParameters.CameraVector;
|
||||
float WaterHeightAboveSample = max(0.0, MaterialParameters.AbsoluteWorldPosition.z - WP.z);
|
||||
float3 TransmittanceToLightThroughWater = 1.0; // no self shadow, same energy as above analytical solution
|
||||
//float3 TransmittanceToLightThroughWater = exp(-ExtinctionCoeff * WaterHeightAboveSample); // self shadow as transmittance to water level, close to reference, depends a bit on sample count due to first sample being critical for dense medium
|
||||
|
||||
float3 SampleTransmittance = exp(-ExtinctionCoeff * RayMarchStepSize); // Constant
|
||||
float3 SS = (ScatteringCoeff * TransmittanceToLightThroughWater * (SunScattLuminance * Shadow + AmbScattLuminance));
|
||||
ScatteredLuminance += Transmittance * (SS - SS * SampleTransmittance) / ExtinctionCoeffSafe;
|
||||
Transmittance *= SampleTransmittance;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The rest of the medium
|
||||
const float3 OpticalDepth2 = ExtinctionCoeff * max(0.0, BehindWaterDeltaDepth - RayMarchMaxDistance);
|
||||
if (any(OpticalDepth2 > 0.0f))
|
||||
{
|
||||
float3 Transmittance2 = exp(-OpticalDepth2);
|
||||
float3 ScatteredLuminance2 = ScatteringCoeff * (SunScattLuminance + AmbScattLuminance);
|
||||
ScatteredLuminance += Transmittance * (ScatteredLuminance2 - ScatteredLuminance2 * Transmittance2) / ExtinctionCoeffSafe;
|
||||
Transmittance *= Transmittance2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply Fresnel effect to out-scattering towards the view
|
||||
ScatteredLuminance *= CameraIsUnderWater ? 1.0 : (1.0 - EnvBrdf); // Under water is less visible due to Fresnel effect
|
||||
Transmittance *= CameraIsUnderWater ? (1.0 - EnvBrdf) : 1.0; // Above " " " " "
|
||||
|
||||
// Add single in-scattering apply colored transmittance to scene color
|
||||
Output.Luminance = WaterVisibility * (ScatteredLuminance + Transmittance * (BehindWaterSceneLuminance* ColorScaleBehindWater));
|
||||
Output.WaterToSceneTransmittance = Transmittance;
|
||||
Output.WaterToSceneToLightTransmittance = Transmittance * MeanTransmittanceToLightSources;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
海洋是不透明的,使用SceneColor缓存合成出的透明效果。
|
||||
|
||||
## GDC2012 神秘海域3演讲
|
||||
### 渲染方案
|
||||
|
||||
### FlowShader
|
||||
没看懂,为什么需要用2张贴图叠加,是因为要过度么?
|
||||
|
||||
4.5.1.1 Flow Map变体:《神秘海域3》Flow Map + Displacement
|
||||
另外,Flow Map可以和其他渲染技术结合使用,比如《神秘海域3》中的Flow Map + Displacement:
|
||||
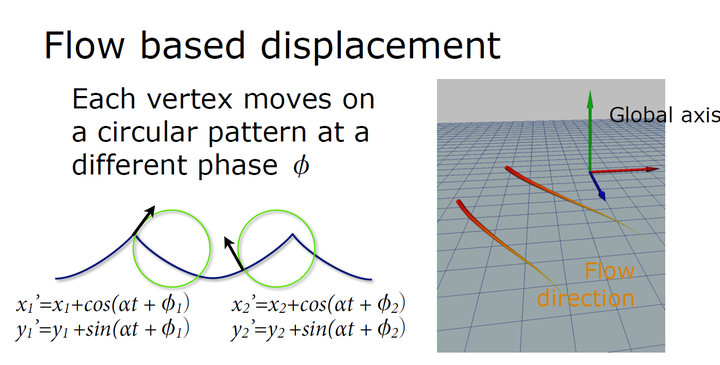
|
||||
|
||||
4.5.1.2 Flow Map变体:《堡垒之夜》Flow Map + Distance Fields + Normal Maps
|
||||
以及《堡垒之夜》中的Flow Map + Distance Fields + Normal Maps [GDC 2019, Technical Artist Bootcamp Distance Fields and Shader Simulation Tricks]
|
||||
|
||||
4.5.1.3 Flow Map变体:《神秘海域4》Flow Map + Wave Particles
|
||||
或者《神秘海域4》中的Flow Map + Wave Particles[SIGGRAPH 2016, Rendering Rapids in Uncharted 4],都是进阶模拟水体表面流动与起伏效果的不错选择。
|
||||
|
||||
### Wave System
|
||||
如果我们能找到一个好的模型,程序化的几何和动画是不错的。
|
||||
仿真计算成本太高(即使在SPU中),设计者也很难控制。
|
||||
Perlin噪音效果在视觉上不是很好,往往看起来很人工化
|
||||
FFT技术很好,但是参数很难被艺术家控制和调整。也是很难搞好的
|
||||
|
||||
**Gerstner waves**
|
||||
简单易于控制效果,但高频细节不够多,只能叠加几组大浪,否则太消耗资源。
|
||||
|
||||
**FFT Waves**
|
||||
真实,细节丰富。但是美术难以控制效果。
|
||||
|
||||
神秘海域3采用4组Gerstner waves+4组波动粒子的方式来实现Wave Vector Displacement。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 大浪
|
||||
大浪采用贝塞尔曲线建模完成
|
||||
**之后再叠加大浪**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是整个波系的局部公式。
|
||||
bspline是一个均匀的、非理性的bspline。我们本可以使用贝塞尔,但它需要更多的代码。
|
||||
grid(u,v)函数返回一个给定坐标u,v的标量值。在这种情况下,我们有一个波标的乘数
|
||||
|
||||
## Sea of Thieves approach [Ang, 2018]
|
||||
|
||||
## Crest Siggraph2019
|
||||
### Light Scattering
|
||||
使用了类似盗贼之海的光线散射算法,光线散射项是基于海面置换项的水平长度。这里补充一下:使它在我们的框架中更好地工作--我们通过将置换项除以波长来做一种特殊的归一化,并将这个归一化版本用于光散射项。
|
||||
|
||||
基于海平面高度的散射在海洋参数发生改变时容易出问题。
|
||||
|
||||
如果将置换项除以波长,就可以针对大波与小波进行缩放。
|
||||
|
||||
### Shadering
|
||||
Cascade scale used to scale shading inputs
|
||||
Normals
|
||||
Foam
|
||||
Underwater bubbles
|
||||
Works for range of viewpoints
|
||||
Breaks up patterns
|
||||
Combats mipmapping
|
||||
Increase visible range of detail
|
||||
Doubles texture samples
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user