36 KiB
title, date, excerpt, tags, rating
| title | date | excerpt | tags | rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VirtualTexture学习笔记 | 2024-02-20 18:26:49 | ⭐ |
前言
- UE4 Runtime Virtual Texture 实现机制及源码解析:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/143709152
- UE Virtual Texture图文浅析:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/642580472
相关概念
- Virtual Texture:虚拟纹理,以下简称 VT
- Runtime Virtual Texture:UE4 运行时虚拟纹理系统,以下简称 RVT
- VT feedback:存储当前屏幕像素对应的 VT Page 信息,用于加载 VT 数据。
- VT Physical Texture:虚拟纹理对应的物理纹理资源
- PageTable:虚拟纹理页表,用来寻址 VT Physical Texture Page 数据。
- PageTable Texture:包含虚拟纹理页表数据的纹理资源,通过此纹理资源可查询 Physical Texture Page 信息。有些 VT 系统也叫 Indirection Texture,由于本文分析 UE4 VT 的内容,这里采用 UE4 术语。
- PageTable Buffer:包含虚拟纹理页表数据内容的 GPU Buffer 资源。
地址映射
地址映射在Virtual Texture是一个很重要的环节,就是如何将一个Virtual Texture的texel映射到Physical Texture的texel上,这里还需要适配当高分辨率的page没有加载的情况,需要得到已经加载的对应低分辨率的page地址。
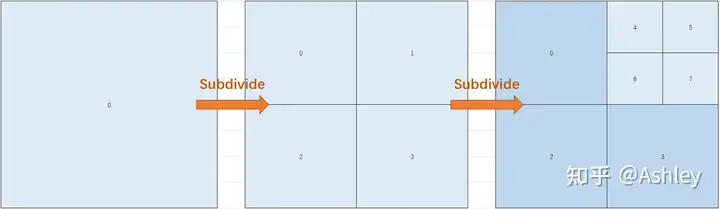
四叉树映射
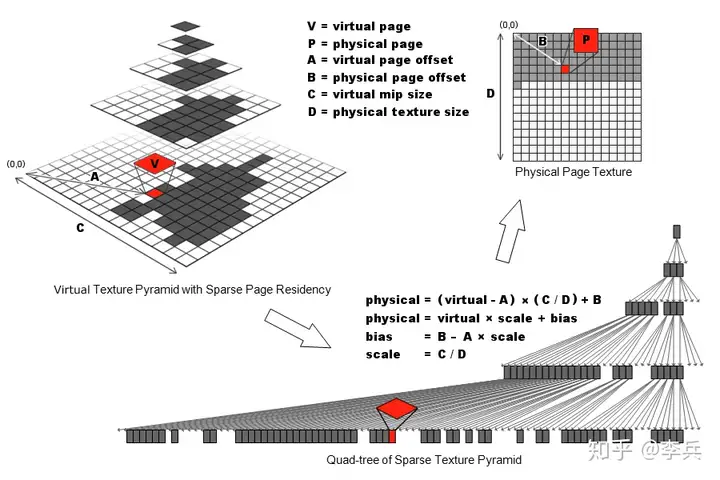 这里每个四叉树的节点的内容存的就是bias和scale,这样就可以将虚拟纹理的地址转换成物理纹理的地址了,假如没有找到,也可以用父节点的地址来得到低分辨率的。但是这里要找到对应的节点需要搜索这个四叉树,搜索的速度取决于树的高度,也就是mipmap的层级,在差的低mip的地址上效率会比较差。
这里每个四叉树的节点的内容存的就是bias和scale,这样就可以将虚拟纹理的地址转换成物理纹理的地址了,假如没有找到,也可以用父节点的地址来得到低分辨率的。但是这里要找到对应的节点需要搜索这个四叉树,搜索的速度取决于树的高度,也就是mipmap的层级,在差的低mip的地址上效率会比较差。
Feedback Rendering
在Virtual Texture中一个很重要的事情是要有一个可以决定加载哪些page的策略,这个策略就是要有一个叫Feedback Rendering的过程。这个可以设计为一个单独的pass,或者跟Pre-Z或者GBuffer同时。渲染生成的这张texture里面存的就是虚纹理的page坐标,mip level和可能的虚纹理id(用来应对多虚纹理的情况)。

可以看到上图,由于page的变化在屏幕空间是比较低的,所以Feedback的RT是不需要全分辨率的,低分辨率渲染就可以了。对于半透明物体或者alpha test的物体,在Feedback Rendering的过程中只能当作是不透明物体来渲染,那样就会在屏幕像素上随机产生当前像素的可能结果。与之相类似的,如果一个屏幕像素用到了两个page,也会是随机出现一种在最后的结果RT上。这样虽然可以让所有需要的page都加载,但是,可能会遇到另外一个问题,那就是可能会发生这一帧加载的page,下一帧的时候被卸载掉了,然后再下一帧又要加载,这样会导致物理纹理一直在置换,即便屏幕像素并未改变,物理纹理的page也无法稳定下来。为了解决这个问题,需要设计一个调色板,对于半透明物体,间隔出现全透明或者不透明,对于多page的情况,则需要设计为间隔出现不同page的结果,这样就能同时加载所有page,并且保持稳定。但是,如果出现了多层半透明物体的叠加或者多个page的情况,如何设计一个合理的调色板变成了一个问题。这里可以考虑为每个像素匹配一个linked list,这个需要额外的硬件支持,叫structured append and consume buffers。
接着就是对这个Feedback的结果进行分析了,分析需要将Feedback的结果读回CPU,这里可以使用compute shader解析这个结果,然后输出到一个更简单的buffer上去:
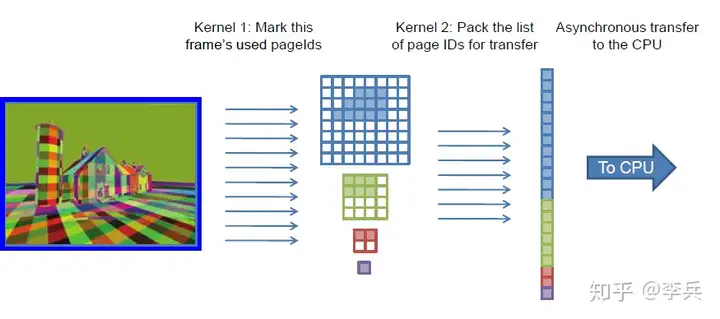
这样可以使回读操作更快,处理page更新也能更快。对于如何更新page,也需要策略,我们需要尽量不阻塞执行,异步的加载page,但是对于完全不存在任何一个mip的page,我们还是需要同步加载防止显示出错。在异步的过程中,我们需要对需要加载page设置优先级,比如需要加载的mip level和已经存在的mip level相差越大的优先级越高,被越多像素要求加载的page的优先级越高,这里需要设计一个完整的加载策略。
Texture Poping
由于page是异步加载的,这是有延时的,当加载的mip比当前显示的差很远的时候,我们渲染会使用新加载的更清晰的mip,这样我们会看到非常明显的跳变。假如我们用了软实现的Tri-linear Filtering,那么当加载的mip level跟当前显示的mip level相差很大的时候,需要做一个delay,等待中间的mip page的加载,然后再去更新。对于没有Tri-linear Filtering的实现,就得逐渐更新page,使得过度平滑。一个可能的方法是,upsample低分辨率的mip,直到高分辨率的mip加载。但是,这样仍然会出现跳变,由于采样的位置其实发生了突变。
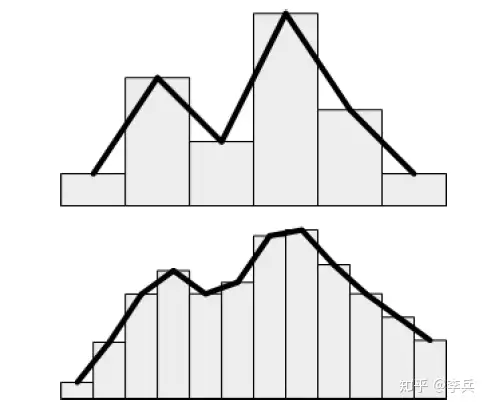
上图可以看到,当分辨率增加2倍之后,结果会发生很大的不同。解决的方案是,先把upsample的低分辨率page加载到一个物理纹理的page,当高分辨率的加载好了,插值过度那个物理纹理的page,这样采样的位置没有发生改变,只是每个像素的颜色在渐变,就不会有跳变出现了。
UE5VirtualTexture相关实现
为读向往大佬文章的学习笔记。
VT 系统概述
从原理上来说,VT 系统主要由 2 大阶段构成,VT 数据准备和 VT 运行时采样阶段。
- VT 数据准备阶段:
- 生成 VT feedback 数据
- 生成 VT 纹理数据,并更新到指定 VT Physical Texture 对应的 Page
- 根据 feedback 数据生成并更新 PageTable 数据
- VT 运行时采样阶段:
- 根据屏幕空间坐标以及相关信息生成 VT Physical Texture UV
- 对 VT Physical Texture 执行采样
UE4 的 RVT 基本上也是按照这个原理和流程来实现的,本文就按照这个顺序来详细讲解。在讲解之前,为了便于后续理解,先来了解下 UE5 RVT 的实现机制。
UE5 RVT 实现机制概述
IVirtualTexture 是 UE5 VT 最重要的接口,它是如何产生 VT 数据的接口,主要有两个抽象函数
- RequestPageData,请求页面数据
- ProducePageData,产生页面数据
在UE5中其子类有:
- FLightmapPreviewVirtualTexture
- FNullVirtualTextureProducer
- FRuntimeVirtualTextureProducer
- FUploadingVirtualTexture
- FVirtualTextureAddressRedirect
- FVirtualTextureLevelRedirector
对于 RVT 来说,实现此接口的是 FRuntimeVirtualTextureProducer,也就是作为运行时产生 Page 纹理数据的类,对于 SVT 来说,实现此接口的是 FUploadingVirtualTexture,用于从磁盘中流送上传 Page 纹理数据。 FVirtualTextureSystem 是全局单件类,包含了 UE5 VT 系统中大部分核心逻辑和流程,驱动这个系统工作的是 Update 函数,分别在 PC/Console Pipeline 的 FDeferredShadingSceneRenderer::Render 和 Mobile Pipeline 的 FMobileSceneRenderer::Render 中调用.
在 VT 中只有 Diffuse 是远远不够的,在实际的着色过程中经常需要其它的纹理数据来进行光照计算,比如 Normal、Roughness、Specular 等等,UE4 的 RVT 使用了 Layer 的概念,每个 Layer 代表不同的 Physical Texture,在 UE4 中可以支持底色(Diffuse)、法线(Normal)、Roughness(粗糙度)、高光度(Specular)、遮罩(Mask)等不同内容的 VT,这些数据以 Pack 的方式保存在多张 Physical Texture 的不同通道中,在使用时通过 Unpack 以及组合的形式解算出来进行光照计算。这些 Physical Texture 的寻址信息保存在同一个 VT 上的 PageTable Texture 的不同颜色通道中,下文会详细描述。
UE4 RVT 中所使用的 GPU 资源有以下 3 种:
- PageTable Buffer 用于在 CPU 端只写的 PageTable 数据。
- PageTable Texture 用于在采样 VT 时获取指定 VT Physical Texture Page 数据,此资源数据不是在 CPU 端填充,而是由 PageTable Buffer 通过 RHICommandList 在 GPU 上填充。
- VT Physical Texture 实际存储纹理数据的资源,通过 VT feedback 从磁盘或运行时动态生成纹理数据,并在 VT 数据准备阶段中更新到 VT Physical Texture 中。
其中 VT Physical Texture 资源包含在 FVirtualTexturePhysicalSpace 类中,PageTable Buffer/Texture 包含在 FVirtualTextureSpace 类中。
FVirtualTextureSystem的会提交请求最终会调用FRuntimeVirtualTextureProducer::ProducePageData() ,最后会在FRuntimeVirtualTextureFinalizer::Finalize() 中 调用 RuntimeVirtualTexture::RenderPages() 函数渲染到 VT Physical Texture 上。
UE5中相关类
- FVirtualTextureSystem:单例类,用于全局控制VT流程。
- URuntimeVirtualTexture(UObject)
- FRuntimeVirtualTextureRenderResource
- UVirtualTexture(UObject)
- UVirtualTexture2D(UTexture2D)
UE5 VirtualHeightfieldMesh简述
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/575398476
可能的相关类
- VirtualHeightfieldMesh
- UVirtualHeightfieldMeshComponent
- UHeightfieldMinMaxTexture
- BuildTexture()
- UHeightfieldMinMaxTexture
- FVirtualHeightfieldMeshSceneProxy
- FVirtualHeightfieldMeshRendererExtension
- AddWork()
- SubmitWork()
- FVirtualTextureFeedbackBuffer 参考#Pass1的补充VirtualTextureFeedback
- UVirtualHeightfieldMeshComponent
- UNiagaraDataInterfaceLandscape
- UNiagaraDataInterfaceVirtualTexture(NiagaraDataInterfaceVirtualTextureTemplate.ush)
- GetAttributesValid()
- SampleRVTLayer()
- SampleRVT()
- URuntimeVirtualTextureComponent
VirtualHeightfieldMesh
首先是MinMaxTexture。全称UHeightfieldMinMaxTexture(下简称MinMaxTexture),可以说是整个VHM中最重要的部分之一。它是离线生成的,目的主要是以下几个:
- 用作Instance的剔除(遮挡剔除查询+Frustum剔除)
- 用作决定VHM的LOD
- 用作平滑VHM的顶点位置
其中比较关键的几个成员变量为:
- TObjectPtr Texture:BGRA8格式、贴图大小与RVT的Tile数量一致、有全部mipmap。每个像素存储RVT一个Tile中的最小值以及最大值,各为16bit、encode在RGBA的4个通道上。
- TObjectPtr LodBiasTexture:G8格式、贴图大小与RTV的Tile数量一致、无mipmap。每个像素存储了Texture对应像素周围3x3blur之后的结果。
- TObjectPtr LodBiasMinMaxTexture:BGRA8格式、贴图大小与RTV的Tile数量一致、有全部mipmap。类似于HZB、每个像素存储LodBiasTexture的最小值以及最大值,各为8bit、存在RG两个通道上。
- int32 MaxCPULevels:表示共需要在CPU端存储多少层level的数据。
- TArray
<FVector2D>TextureData:CPU端存储Texture贴图的数据,共MaxCPULevels层mipmap。
TextureData的获取
因此要生成MinMaxTexture、最关键的就是要得到TextureData,其入口函数为位于HeightfieldMinMaxTextureBuilder.cpp的VirtualHeightfieldmesh::BuildMinMaxTexture中。由于Texture存储的是RVT中每个Tile中最小最大值,因此不难想象到其大致流程可以分为以下几步:
- 遍历RVT的每个Tile并绘制到一张中间贴图上,然后计算这张中间纹理的最小最大值、存储至目标贴图对应的位置上;
- 为目标贴图生成mipmap;
- 将目标贴图回读至CPU、得到TextureData。
将Tile绘制到一张中间贴图使用的是自带的RuntimeVirtualTexture::RenderPagesStandAlone函数;计算最小最大值是通过Downsample的方式计算而成。如下图所示为2x2Tiles、4TileSize的RVT,计算Tile0的最小最大值的示意过程图:
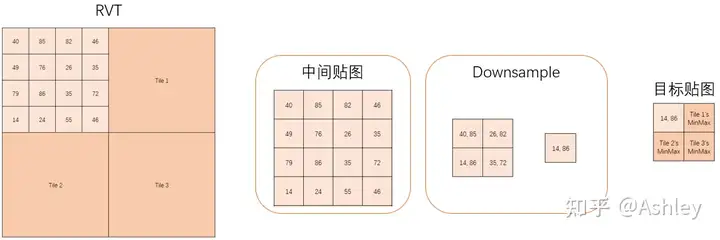
Downsample的ComputeShader为TMinMaxTextureCS。遍历计算完每个Tile的最小最大值后,同样通过Downsample为目标贴图生成全mipmap。
最后为了将贴图回读到CPU,先是通过CopyTexture的方式将目标贴图的各个mipmap复制到各自带有CPUReadback Flag的贴图后,再通过MapStagingSurface/UnmapStagingSurface的方式复制到CPU内存上。由于是比较常规的操作,就不过多介绍了。
至此也就得到了带有所有mipmap的CPU端的TextureData,接着将此作为参数调用UHeightfieldMinMaxTexture::BuildTexture以生成剩下的内容(即Texture、LodBiasTexture、LodBiasMinMaxTexture)。
FVirtualHeightfieldMeshSceneProxy
至此离线生成的MinMaxTexture介绍完毕,后面都是实时渲染内容的介绍部分。所有内容都围绕着VHM的SceneProxy也就是FVirtualHeightfieldMeshSceneProxy展开。
遮挡剔除
关于硬件的遮挡剔除用法可以参考DX12的官方sample[8]
首先是遮挡剔除部分,VHM做了Tile级别且带有LOD的遮挡剔除。VHM的SceneProxy重写了函数GetOcclusionQueries,函数实现只是简单地返回OcclusionVolumes:
 OcclusionVolumes的构建在函数BuildOcclusionVolumes中,其基本思路为取MinMaxTexture中CPU端的TextureData的数据、获得每个Tile的高度最小最大值来创建该Tile的Bounds信息。
OcclusionVolumes的构建在函数BuildOcclusionVolumes中,其基本思路为取MinMaxTexture中CPU端的TextureData的数据、获得每个Tile的高度最小最大值来创建该Tile的Bounds信息。
可以看到OcclusionVolumes是带有Lod的。当然实际上这里的代码的LodIndex不一定从0开始,因为Component中有一项成员变量NumOcclusionLod、表示创建多少层mipmap的OcclusionVolumes。另外有一点需要注意的是,NumOcclusionLod默认值为0、也就是说VHM的遮挡剔除默认没有开启。

由于VHM需要在ComputePass中动态地构建Instance绘制的IndirectArgs、因此SceneProxy还重写了函数AcceptOcclusionResults,用以获取遮挡剔除的结果。具体是将UE返回的遮挡剔除的结果存在贴图OcclusionTexture上、以便能够作为SRV在后续的Pass中访问:
void FVirtualHeightfieldMeshSceneProxy::AcceptOcclusionResults(FSceneView const* View, TArray<bool>* Results, int32 ResultsStart, int32 NumResults)
{
// 由于构建IndirectArgs跟SceneProxy不在同一个地方,因此用了一个全局变量来保存遮挡剔除的结果
FOcclusionResults& OcclusionResults = GOcclusionResults.Emplace(FOcclusionResultsKey(this, View));
OcclusionResults.TextureSize = OcclusionGridSize;
OcclusionResults.NumTextureMips = NumOcclusionLods;
// 创建贴图,并将遮挡剔除结果Copy至贴图上
FRHIResourceCreateInfo CreateInfo(TEXT("VirtualHeightfieldMesh.OcclusionTexture"));
OcclusionResults.OcclusionTexture = RHICreateTexture2D(OcclusionGridSize.X, OcclusionGridSize.Y, PF_G8, NumOcclusionLods, 1, TexCreate_ShaderResource, CreateInfo);
bool const* Src = Results->GetData() + ResultsStart;
FIntPoint Size = OcclusionGridSize;
for (int32 MipIndex = 0; MipIndex < NumOcclusionLods; ++MipIndex)
{
uint32 Stride;
uint8* Dst = (uint8*)RHILockTexture2D(OcclusionResults.OcclusionTexture, MipIndex, RLM_WriteOnly, Stride, false);
for (int Y = 0; Y < Size.Y; ++Y)
{
for (int X = 0; X < Size.X; ++X)
{
Dst[Y * Stride + X] = *(Src++) ? 255 : 0;
}
}
RHIUnlockTexture2D(OcclusionResults.OcclusionTexture, MipIndex, false);
Size.X = FMath::Max(Size.X / 2, 1);
Size.Y = FMath::Max(Size.Y / 2, 1);
}
}
整体思路
至此就开始真正的VHM的Mesh的数据构建了。为了后续的代码细节能够更加易懂,这里再说明一下VHM构建mesh的整体思路:假设我们有一个工作队列为QueueBuffer,每一项工作就是从QueueBuffer中取出一项工作(更准确地说,取出一个Quad)、对这个Quad判断是否需要进行细化、如果需要细分则将这个Quad细分为4个Quad并塞入QueueBuffer中。
重复这个取出→处理→放回的过程,直到QueueBuffer中没有工作为止。示意图如下:
RVT相关代码(Pass1:CollectQuad)
如果不能细分,那么就会增加一个Instance、将其Instance的数据写入RWQuadBuffer中。RWQuadBuffer将会用在后续的CullInstance Pass中,以真正地构建IndirectArgs:
// 无法继续细分的情况
// 用以后续对RVT进行采样
uint PhysicalAddress = PageTableTexture.Load(int3(Pos, Level));
InterlockAdd(RWQuadInfo.Write, 1, Write);
RWQuadBuffer[Write] = Pack(InitQuadRenderItem(Pos, Level, PhysicalAddress, bCull | bOcclude));
其中的RWQuadInfo是我编的变量名、实际的代码中并不存在。或者说实际上这里的变量名是RWIndirectArgsBuffer,但是并不是前面所说的用以绘制的IndirectArgs。为了不让大家混淆,这里改了下变量名
另外也能由此看出的是,VHM也许曾经想过利用IndirectArgs数组来绘制(即DXSample中将符合条件的生成IndirectArgs放进数组中)。但是最后改成的是一个IndirectArgs但是Instance的绘制方式
PS. PageTableTexture的类型为RHITextuire。相关Shader代码位于VirtualHeightfieldMesh.usf
Pass1的补充VirtualTextureFeedback
不再继续进行细分后、说明后续就要对该Level的RVT进行采样,因此需要处理对应的Feedback信息、让虚幻可以加载对应的Page。shader代码如下图所示:
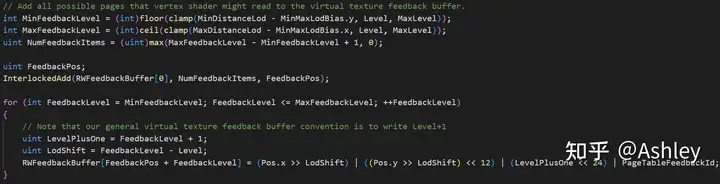
c++中则要将这个RWFeedbackBuffer喂给虚幻的函数SubmitVirtualTextureFeedbackBuffer:

相关代码段
FVertexFactoryIntermediates GetVertexFactoryIntermediates(FVertexFactoryInput Input)
{
...
// Sample height from virtual texture.
VTUniform Uniform = VTUniform_Unpack(VHM.VTPackedUniform);
Uniform.vPageBorderSize -= .5f * VHM.PhysicalTextureSize.y; // Half texel offset is used in VT write and in sampling because we want texel locations to match landscape vertices.
VTPageTableUniform PageTableUniform = VTPageTableUniform_Unpack(VHM.VTPackedPageTableUniform0, VHM.VTPackedPageTableUniform1);
VTPageTableResult VTResult0 = TextureLoadVirtualPageTableLevel(VHM.PageTableTexture, PageTableUniform, NormalizedPos, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, floor(SampleLevel));
float2 UV0 = VTComputePhysicalUVs(VTResult0, 0, Uniform);
float Height0 = VHM.HeightTexture.SampleLevel(VHM.HeightSampler, UV0, 0);
VTPageTableResult VTResult1 = TextureLoadVirtualPageTableLevel(VHM.PageTableTexture, PageTableUniform, NormalizedPos, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, ceil(SampleLevel));
float2 UV1 = VTComputePhysicalUVs(VTResult1, 0, Uniform);
float Height1 = VHM.HeightTexture.SampleLevel(VHM.HeightSampler, UV1, 0);
float Height = lerp(Height0.x, Height1.x, frac(SampleLevel));
...
}
渲染线程创建VT的相关逻辑:
void FVirtualHeightfieldMeshSceneProxy::CreateRenderThreadResources()
{
if (RuntimeVirtualTexture != nullptr)
{
if (!bCallbackRegistered)
{
GetRendererModule().AddVirtualTextureProducerDestroyedCallback(RuntimeVirtualTexture->GetProducerHandle(), &OnVirtualTextureDestroyedCB, this);
bCallbackRegistered = true;
}
//URuntimeVirtualTexture* RuntimeVirtualTexture;
if (RuntimeVirtualTexture->GetMaterialType() == ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType::WorldHeight)
{
AllocatedVirtualTexture = RuntimeVirtualTexture->GetAllocatedVirtualTexture();
NumQuadsPerTileSide = RuntimeVirtualTexture->GetTileSize();
if (AllocatedVirtualTexture != nullptr)
{
// Gather vertex factory uniform parameters.
FVirtualHeightfieldMeshVertexFactoryParameters UniformParams;
UniformParams.PageTableTexture = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPageTableTexture(0);
UniformParams.HeightTexture = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPhysicalTextureSRV(0, false);
UniformParams.HeightSampler = TStaticSamplerState<SF_Bilinear>::GetRHI();
UniformParams.LodBiasTexture = LodBiasTexture ? LodBiasTexture->GetResource()->TextureRHI : GBlackTexture->TextureRHI;
UniformParams.LodBiasSampler = TStaticSamplerState<SF_Point>::GetRHI();
UniformParams.NumQuadsPerTileSide = NumQuadsPerTileSide;
FUintVector4 PackedUniform;
AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPackedUniform(&PackedUniform, 0);
UniformParams.VTPackedUniform = PackedUniform;
FUintVector4 PackedPageTableUniform[2];
AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPackedPageTableUniform(PackedPageTableUniform);
UniformParams.VTPackedPageTableUniform0 = PackedPageTableUniform[0];
UniformParams.VTPackedPageTableUniform1 = PackedPageTableUniform[1];
const float PageTableSizeX = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetWidthInTiles();
const float PageTableSizeY = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetHeightInTiles();
UniformParams.PageTableSize = FVector4f(PageTableSizeX, PageTableSizeY, 1.f / PageTableSizeX, 1.f / PageTableSizeY);
const float PhysicalTextureSize = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPhysicalTextureSize(0);
UniformParams.PhysicalTextureSize = FVector2f(PhysicalTextureSize, 1.f / PhysicalTextureSize);
UniformParams.VirtualHeightfieldToLocal = FMatrix44f(UVToLocal);
UniformParams.VirtualHeightfieldToWorld = FMatrix44f(UVToWorld); // LWC_TODO: Precision loss
UniformParams.MaxLod = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetMaxLevel();
UniformParams.LodBiasScale = LodBiasScale;
// Create vertex factory.
VertexFactory = new FVirtualHeightfieldMeshVertexFactory(GetScene().GetFeatureLevel(), UniformParams);
VertexFactory->InitResource(FRHICommandListImmediate::Get());
}
}
}
}
RVT生成相关
RVT相关操作总结
CPU端创建:
作为UniformParameter传递到GPU端:
AllocatedVirtualTexture = RuntimeVirtualTexture->GetAllocatedVirtualTexture();
//PageTableTexture、Texture&Sampler
FVirtualHeightfieldMeshVertexFactoryParameters UniformParams;
UniformParams.PageTableTexture = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPageTableTexture(0);
UniformParams.HeightTexture = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPhysicalTextureSRV(0, false);
UniformParams.HeightSampler = TStaticSamplerState<SF_Bilinear>::GetRHI();
//VTPackedUniform&VTPackedPageTableUniform
FUintVector4 PackedUniform;
AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPackedUniform(&PackedUniform, 0);
UniformParams.VTPackedUniform = PackedUniform;
FUintVector4 PackedPageTableUniform[2];
AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPackedPageTableUniform(PackedPageTableUniform);
UniformParams.VTPackedPageTableUniform0 = PackedPageTableUniform[0];
UniformParams.VTPackedPageTableUniform1 = PackedPageTableUniform[1];
//PageTableSize
const float PageTableSizeX = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetWidthInTiles();
const float PageTableSizeY = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetHeightInTiles();
UniformParams.PageTableSize = FVector4f(PageTableSizeX, PageTableSizeY, 1.f / PageTableSizeX, 1.f / PageTableSizeY);
//PhysicalTextureSize
const float PhysicalTextureSize = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetPhysicalTextureSize(0);
UniformParams.PhysicalTextureSize = FVector2f(PhysicalTextureSize, 1.f / PhysicalTextureSize);
//Local <=> World Matrix
UniformParams.VirtualHeightfieldToLocal = FMatrix44f(UVToLocal);
UniformParams.VirtualHeightfieldToWorld = FMatrix44f(UVToWorld); // LWC_TODO: Precision loss
//MaxLod
UniformParams.MaxLod = AllocatedVirtualTexture->GetMaxLevel();
GPU端采样:
VTUniform Uniform = VTUniform_Unpack(VHM.VTPackedUniform);
Uniform.vPageBorderSize -= .5f * VHM.PhysicalTextureSize.y; // Half texel offset is used in VT write and in sampling because we want texel locations to match landscape vertices.
VTPageTableUniform PageTableUniform = VTPageTableUniform_Unpack(VHM.VTPackedPageTableUniform0, VHM.VTPackedPageTableUniform1);
VTPageTableResult VTResult0 = TextureLoadVirtualPageTableLevel(VHM.PageTableTexture, PageTableUniform, NormalizedPos, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, floor(SampleLevel));
float2 UV0 = VTComputePhysicalUVs(VTResult0, 0, Uniform);
float Height0 = VHM.HeightTexture.SampleLevel(VHM.HeightSampler, UV0, 0);
VTPageTableResult VTResult1 = TextureLoadVirtualPageTableLevel(VHM.PageTableTexture, PageTableUniform, NormalizedPos, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, ceil(SampleLevel));
float2 UV1 = VTComputePhysicalUVs(VTResult1, 0, Uniform);
float Height1 = VHM.HeightTexture.SampleLevel(VHM.HeightSampler, UV1, 0);
float Height = lerp(Height0.x, Height1.x, frac(SampleLevel));
NiagaraDataInterfaceVirtualTextureTemplate.ush中的代码:
//其他相关VT操作函数位于VirtualTextureCommon.ush
float4 SampleRVTLayer_{ParameterName}(float2 SampleUV, Texture2D InTexture, Texture2D<uint4> InPageTable, uint4 InTextureUniforms)
{
VTPageTableResult PageTable = TextureLoadVirtualPageTableLevel(InPageTable, VTPageTableUniform_Unpack({ParameterName}_PageTableUniforms[0], {ParameterName}_PageTableUniforms[1]), SampleUV, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, VTADDRESSMODE_CLAMP, 0.0f);
return TextureVirtualSample(InTexture, {ParameterName}_SharedSampler, PageTable, 0, VTUniform_Unpack(InTextureUniforms));
}
void SampleRVT_{ParameterName}(in float3 WorldPosition, out bool bInsideVolume, out float3 BaseColor, out float Specular, out float Roughness, out float3 Normal, out float WorldHeight, out float Mask)
{
bInsideVolume = false;
BaseColor = float3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Specular = 0.5f;
Roughness = 0.5f;
Normal = float3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
WorldHeight = 0.0f;
Mask = 1.0f;
// Get Sample Location
FLWCVector3 LWCWorldPosition = MakeLWCVector3({ParameterName}_SystemLWCTile, WorldPosition);
FLWCVector3 LWCUVOrigin = MakeLWCVector3({ParameterName}_SystemLWCTile, {ParameterName}_UVUniforms[0].xyz);
float2 SampleUV = VirtualTextureWorldToUV(LWCWorldPosition, LWCUVOrigin, {ParameterName}_UVUniforms[1].xyz, {ParameterName}_UVUniforms[2].xyz);
// Test to see if we are inside the volume, but still take the samples as it will clamp to the edge
bInsideVolume = all(SampleUV >- 0.0f) && all(SampleUV < 1.0f);
// Sample Textures
float4 LayerSample[3];
LayerSample[0] = ({ParameterName}_ValidLayersMask & 0x1) != 0 ? SampleRVTLayer_{ParameterName}(SampleUV, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture0, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture0PageTable, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture0TextureUniforms) : 0;
LayerSample[1] = ({ParameterName}_ValidLayersMask & 0x2) != 0 ? SampleRVTLayer_{ParameterName}(SampleUV, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture1, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture1PageTable, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture1TextureUniforms) : 0;
LayerSample[2] = ({ParameterName}_ValidLayersMask & 0x4) != 0 ? SampleRVTLayer_{ParameterName}(SampleUV, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture2, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture2PageTable, {ParameterName}_VirtualTexture2TextureUniforms) : 0;
// Sample Available Attributes
switch ( {ParameterName}_MaterialType )
{
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_BaseColor:
{
BaseColor = LayerSample[0].xyz;
break;
}
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_BaseColor_Normal_Roughness:
{
BaseColor = VirtualTextureUnpackBaseColorSRGB(LayerSample[0]);
Roughness = LayerSample[1].y;
Normal = VirtualTextureUnpackNormalBGR565(LayerSample[1]);
break;
}
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_BaseColor_Normal_DEPRECATED:
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_BaseColor_Normal_Specular:
{
BaseColor = LayerSample[0].xyz;
Specular = LayerSample[1].x;
Roughness = LayerSample[1].y;
Normal = VirtualTextureUnpackNormalBC3BC3(LayerSample[0], LayerSample[1]);
break;
}
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_BaseColor_Normal_Specular_YCoCg:
{
BaseColor = VirtualTextureUnpackBaseColorYCoCg(LayerSample[0]);
Specular = LayerSample[2].x;
Roughness = LayerSample[2].y;
Normal = VirtualTextureUnpackNormalBC5BC1(LayerSample[1], LayerSample[2]);
break;
}
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_BaseColor_Normal_Specular_Mask_YCoCg:
{
BaseColor = VirtualTextureUnpackBaseColorYCoCg(LayerSample[0]);
Specular = LayerSample[2].x;
Roughness = LayerSample[2].y;
Normal = VirtualTextureUnpackNormalBC5BC1(LayerSample[1], LayerSample[2]);
Mask = LayerSample[2].w;
break;
}
case ERuntimeVirtualTextureMaterialType_WorldHeight:
{
WorldHeight = VirtualTextureUnpackHeight(LayerSample[0], {ParameterName}_WorldHeightUnpack);
break;
}
}
}
RVT的UV计算逻辑在VirtualTextureWorldToUV()中:
float2 VirtualTextureWorldToUV(in float3 WorldPos, in float3 Origin, in float3 U, in float3 V)
{
float3 P = WorldPos - Origin;
return saturate(float2(dot(P, U), dot(P, V)));
}
从代码可以看出,根据当前像素的世界空间位置以及 RVT Volume 原点(Volume 左下角)、Volume 边界大小的 UV 范围(经过世界旋转变换的 XY 轴乘以 Volume 缩放-即 Volume 大小-的倒数,这些计算在 URuntimeVirtualTexture::Initialize() 中完成),求出当前像素在 RVT 中的 UV 坐标。
TextureComputeVirtualMipLevel() 函数计算 RVT 的 mipLevel,为了实现较好的混合效果,这里根据当前帧 Id 生成交错的随机 noise 扰动 level。
int TextureComputeVirtualMipLevel(
in out VTPageTableResult OutResult,
float2 dUVdx, float2 dUVdy, float MipBias,
float2 SvPositionXY,
VTPageTableUniform PageTableUniform)
{
OutResult.dUVdx = dUVdx * PageTableUniform.SizeInPages;
OutResult.dUVdy = dUVdy * PageTableUniform.SizeInPages;
// Always compute mip level using MipLevelAniso2D, even if VIRTUAL_TEXTURE_ANISOTROPIC_FILTERING is disabled
// This way the VT mip level selection will come much closer to HW mip selection, even if we're not sampling the texture using anisotropic filtering const float ComputedLevel = MipLevelAniso2D(OutResult.dUVdx, OutResult.dUVdy, PageTableUniform.MaxAnisoLog2);
const float GlobalMipBias = GetGlobalVirtualTextureMipBias();
#if VIRTUAL_TEXTURE_MANUAL_TRILINEAR_FILTERING
const float Noise = 0.f;
#else
const float Noise = GetStochasticMipNoise(SvPositionXY);
#endif
const float MipLevel = ComputedLevel + MipBias + GlobalMipBias + Noise;
const float MipLevelFloor = floor(MipLevel);
OutResult.MipLevelFrac = MipLevel - MipLevelFloor;
return (int)MipLevelFloor + int(PageTableUniform.vPageTableMipBias);
}
TextureLoadVirtualPageTableInternal 函数代码如下:
void TextureLoadVirtualPageTableInternal(
in out VTPageTableResult OutResult,
Texture2D<uint4> PageTable0, Texture2D<uint4> PageTable1,
VTPageTableUniform PageTableUniform,
float2 UV, int vLevel)
{
OutResult.UV = UV * PageTableUniform.SizeInPages;
const uint vLevelClamped = clamp(vLevel, 0, int(PageTableUniform.MaxLevel));
uint vPageX = (uint(OutResult.UV.x) + PageTableUniform.XOffsetInPages) >> vLevelClamped;
uint vPageY = (uint(OutResult.UV.y) + PageTableUniform.YOffsetInPages) >> vLevelClamped;
OutResult.PageTableValue[0] = PageTable0.Load(int3(vPageX, vPageY, vLevelClamped));
OutResult.PageTableValue[1] = PageTable1.Load(int3(vPageX, vPageY, vLevelClamped));
#if VIRTUAL_TEXTURE_MANUAL_TRILINEAR_FILTERING
// Second page table for trilinear.
const uint vLevelClamped2 = clamp(vLevel + 1, 0, int(PageTableUniform.MaxLevel));
const uint vPageX2 = (uint(OutResult.UV.x) + PageTableUniform.XOffsetInPages) >> vLevelClamped2;
const uint vPageY2 = (uint(OutResult.UV.y) + PageTableUniform.YOffsetInPages) >> vLevelClamped2;
OutResult.PageTableValue[2] = PageTable0.Load(int3(vPageX2, vPageY2, vLevelClamped2)); OutResult.PageTableValue[3] = PageTable1.Load(int3(vPageX2, vPageY2, vLevelClamped2));
// Alternate requests to both mip levels
if ((View.FrameNumber & 1u) == 0u)
{ vLevel += 1; vPageX = vPageX2; vPageY = vPageY2; }#endif
// PageTableID packed in upper 4 bits of 'PackedPageTableUniform', which is the bit position we want it in for PackedRequest as well, just need to mask off extra bits
OutResult.PackedRequest = PageTableUniform.ShiftedPageTableID;
OutResult.PackedRequest |= vPageX;
OutResult.PackedRequest |= vPageY << 12;
// Feedback always encodes vLevel+1, and subtracts 1 on the CPU side.
// This allows the CPU code to know when we requested a negative vLevel which indicates that we don't have sufficient virtual texture resolution. const uint vLevelPlusOneClamped = clamp(vLevel + 1, 0, int(PageTableUniform.MaxLevel + 1));
OutResult.PackedRequest |= vLevelPlusOneClamped << 24;
}```
这个函数主要 2个作用,一是生成用于寻址 VT Physical Texture 的 PageTableValue,另一个是生成 feedback Request 数据,具体有以下几个步骤:
1. 根据 UV 寻址模式修正虚拟纹理坐标
2. 根据当前 VT 的 Page 数量和上一步修正过的虚拟纹理坐标计算出 VT 坐标对应的 Page 坐标。
3. 通过 Page 坐标加上 Page 的 XY 偏移,再根据 mipLevel,计算出 PageTable Texture 的 UV 坐标,然后使用这个 UV 坐标和 mipLevel 采样 PageTable Texture 得到在 Physical Texture 上的信息,保存在 PageTableValue 中,在接下来的流程中使用。
4. 将第 3 步计算好的 PageTable Texture 的 Page 坐标和 mipLevel 保存在 VTPageTableResult 中,最后通过 StoreVirtualTextureFeedback 函数写入到 VT feedback Buffer 中。
***TextureVirtualSample***
采样所需的 VTPageTableResult 数据准备完毕,在 TextureVirtualSample 函数中就是执行真正的 Physical Texture 采样逻辑,代码如下:
```c++
MaterialFloat4 TextureVirtualSample(
Texture2D Physical, SamplerState PhysicalSampler,
VTPageTableResult PageTableResult, uint LayerIndex,
VTUniform Uniform)
{
const float2 pUV = VTComputePhysicalUVs(PageTableResult, LayerIndex, Uniform);
return Physical.SampleGrad(PhysicalSampler, pUV, PageTableResult.dUVdx, PageTableResult.dUVdy);
}
这个函数很简单,只有 2 个函数调用,第一行 VTComputePhysicalUVs 用于生成 Physical Texture UV 坐标,第二行用于执行渐变采样,所以这里重点是如何生成 Physical Texture UV 坐标,VTComputePhysicalUVs 函数代码如下:
float2 VTComputePhysicalUVs(in out VTPageTableResult PageTableResult, uint LayerIndex, VTUniform Uniform)
{
const uint PackedPageTableValue = PageTableResult.PageTableValue[LayerIndex / 4u][LayerIndex & 3u];
// See packing in PageTableUpdate.usf
const uint vLevel = PackedPageTableValue & 0xf;
const float UVScale = 1.0f / (float)(1 << vLevel);
const float pPageX = (float)((PackedPageTableValue >> 4) & ((1 << Uniform.PageCoordinateBitCount) - 1));
const float pPageY = (float)(PackedPageTableValue >> (4 + Uniform.PageCoordinateBitCount));
const float2 vPageFrac = frac(PageTableResult.UV * UVScale);
const float2 pUV = float2(pPageX, pPageY) * Uniform.pPageSize + (vPageFrac * Uniform.vPageSize + Uniform.vPageBorderSize);
const float ddxyScale = UVScale * Uniform.vPageSize;
PageTableResult.dUVdx *= ddxyScale;
PageTableResult.dUVdy *= ddxyScale;
return pUV;
}
VT还存在一个反馈机制,具体可以参考:#Pass1的补充VirtualTextureFeedback
/** GPU fence pool. Contains a fence array that is kept in sync with the FeedbackItems ring buffer. Fences are used to know when a transfer is ready to Map() without stalling. */
/** GPU 栅栏池。其中包含一个与 FeedbackItems 环形缓冲区保持同步的栅栏数组。栅栏用于了解传输何时准备就绪,可在不停滞的情况下进行 Map()。 */
class FFeedbackGPUFencePool* Fences;
使用RVT实现3D高斯 LOD思路
AI数据侧:
- 确定点云数据是否可以划分成四叉树的数据结构,也就是将一堆点云按照一个距离阈值 进行分割,最终形成一个四叉树。
- 确定是否可以生成金字塔结构贴图(直接写入到Mipmap结构里),或者生成多张基于2的幕长度贴图。
UE侧: 目前已经测试过SVT可以放入到Niagara Texture Sampler中。同时也可以将SVT放到Texture2DArray中。
- 将3D高斯各种贴图制作成SVT之后塞入Texture2DArray,在Niagara中采样。
- 在Niagara中根据Niagara 粒子ID对SVT进行采样。