4.3 KiB
4.3 KiB
GlobalConfig
- 功能描述: 和Config一样指定该属性可作为配置读取和写入ini中,但只会读取写入到配置文件里基类的值,而不会使用配置文件里子类里的值。
- 元数据类型: bool
- 引擎模块: Config
- 作用机制: 在PropertyFlags中加入CPF_GlobalConfig
- 常用程度: ★★★
和Config一样指定该属性可作为配置读取和写入ini中,但只会读取写入到配置文件里基类的值,而不会使用配置文件里子类里的值。
但是不同点在于,该属性在LoadConfig的时候,只会读取基类的ini,而不会去读取子类的ini。因为只有基类里的Ini设置在生效,相当于全局只有一个配置在生效,因此名字叫做GlobalConfig。
示例代码:
UCLASS(Config = MyOtherGame)
class INSIDER_API UMyProperty_Config :public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite)
int32 MyProperty = 123;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Config)
int32 MyPropertyWithConfig = 123;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, GlobalConfig)
int32 MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig = 123;
};
UCLASS(Config = MyOtherGame)
class INSIDER_API UMyProperty_Config_Child :public UMyProperty_Config
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
};
void UMyProperty_Config_Test::TestConfigSave()
{
FString fileName = FPaths::ProjectConfigDir() / TEXT("MyOtherGame.ini");
fileName = FConfigCacheIni::NormalizeConfigIniPath(fileName);
{
UMyProperty_Config* testObject = NewObject<UMyProperty_Config>(GetTransientPackage(), TEXT("testObject"));
testObject->MyProperty = 777;
testObject->MyPropertyWithConfig = 777;
testObject->MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig = 777;
testObject->SaveConfig(CPF_Config, *fileName);
}
{
UMyProperty_Config_Child* testObject = NewObject<UMyProperty_Config_Child>(GetTransientPackage(), TEXT("testObjectChild"));
testObject->MyProperty = 888;
testObject->MyPropertyWithConfig = 888;
testObject->MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig = 888;
testObject->SaveConfig(CPF_Config, *fileName);
}
}
void UMyProperty_Config_Test::TestConfigLoad()
{
FString fileName = FPaths::ProjectConfigDir() / TEXT("MyOtherGame.ini");
fileName = FConfigCacheIni::NormalizeConfigIniPath(fileName);
UMyProperty_Config* testObject = NewObject<UMyProperty_Config>(GetTransientPackage(), TEXT("testObject"));
testObject->LoadConfig(nullptr, *fileName);
UMyProperty_Config_Child* testObjectChild = NewObject<UMyProperty_Config_Child>(GetTransientPackage(), TEXT("testObjectChild"));
testObjectChild->LoadConfig(nullptr, *fileName);
}
示例效果:
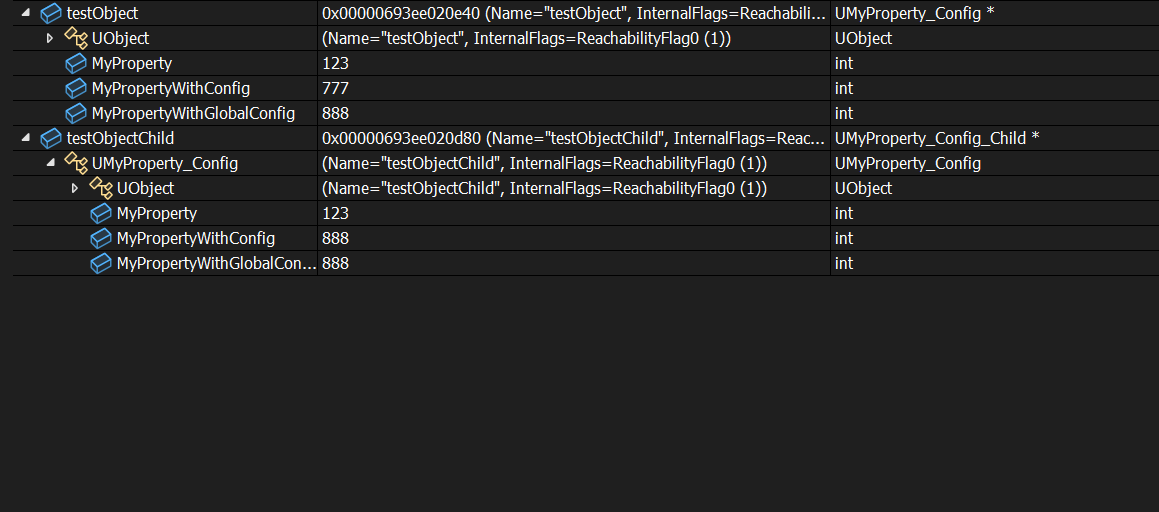
TestConfigSave之后,MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig=888,可见保存的时候也只会保存在基类上。
[/Script/Insider.MyProperty_Config]
MyPropertyWithConfig=777
MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig=888
[/Script/Insider.MyProperty_Config_Child]
MyPropertyWithConfig=888
为了测试,假如手动把配置里的值改为:然后再进行TestConfigLoad测试
[/Script/Insider.MyProperty_Config]
MyPropertyWithConfig=777
MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig=888
[/Script/Insider.MyProperty_Config_Child]
MyPropertyWithConfig=888
MyPropertyWithGlobalConfig=999
显示效果:
可见testObjectChild 的值并没有使用ini里MyProperty_Config_Child下的999的值,而是同样的888.
原理:
如果是bGlobalConfig ,会采用基类。
void UObject::LoadConfig( UClass* ConfigClass/*=NULL*/, const TCHAR* InFilename/*=NULL*/, uint32 PropagationFlags/*=LCPF_None*/, FProperty* PropertyToLoad/*=NULL*/ )
{
const bool bGlobalConfig = (Property->PropertyFlags&CPF_GlobalConfig) != 0;
UClass* OwnerClass = Property->GetOwnerClass();
UClass* BaseClass = bGlobalConfig ? OwnerClass : ConfigClass;
if ( !bPerObject )
{
ClassSection = BaseClass->GetPathName();
LongCommitName = BaseClass->GetOutermost()->GetFName();
// allow the class to override the expected section name
OverrideConfigSection(ClassSection);
}
// globalconfig properties should always use the owning class's config file
// specifying a value for InFilename will override this behavior (as it does with normal properties)
const FString& PropFileName = (bGlobalConfig && InFilename == NULL) ? OwnerClass->GetConfigName() : Filename;
}